In the digital era, automation has moved beyond simple scripts to sophisticated, intelligent systems that fundamentally change how enterprises operate. The initial transformation was driven by the advent of chatbots, which brought automation into conversations and quickly streamlined customer service and employee IT support. Yet, as user expectations grew and interactions became more complex, the limitations of these basic scripted systems became apparent. This evolution led to the emergence of Artificial Intelligence (AI), which redefined automated communication by introducing dynamic learning, contextual understanding, and decision-making capabilities - ushering in the era of the AI agent.
The ServiceNow platform is at the forefront of this shift, leveraging AI and analytics (Now Intelligence) to accelerate digital transformation and move enterprises beyond standard automation. While both are integral to modern business processes, AI agents and chatbots differ significantly in their design, adaptability, and capabilities.
What is a Chatbot?
A chatbot is a software application designed to engage in human-like conversation through text or voice. These programs automate responses, assist with routine inquiries, or perform specific actions, circumventing the need for limited human resources like standard call centers.
Types of Chatbots: Chatbots range from simple, rule-based systems to highly sophisticated, AI-driven assistants. Common types include:
- Menu-based chatbots: Follow a highly structured flow using predefined paths and options.
- Keyword-based chatbots: Identify specific keywords in user input to generate responses, but are limited to a fixed set of terms.
- Rule-based chatbots: Operate strictly within predefined rules and conditions using if/then logic, excelling at structured queries but unable to learn or adapt.
- No code or low code chatbots: Built using user-friendly platforms, relying on templates or rules with minimal programming skills required.
- AI-powered contextual chatbots: Use Natural Language Processing (NLP) and Machine Learning (ML) to dynamically interpret user inputs, understand context, and remember past interactions.
- Hybrid chatbots: Combine structured, rule-based options with adaptive, AI-powered learning.
AI chatbots: Leverage sophisticated AI algorithms for flexible, personalized, and continuously improving interactions.
Common Chatbot Use Cases include simplifying customer service (password resets, order tracking), providing instant answers to FAQs, assisting with reservations and booking, and carrying out routine basic IT support tasks (like unlocking accounts).
What is an AI Agent?
An AI agent is an intelligent software system that operates autonomously within its environment. These agents are capable of gathering data, making decisions, and performing complex, multi-step tasks to achieve specific goals. They adapt dynamically, learn from experiences, and utilize advanced algorithms like Large Language Models (LLMs) to process massive amounts of information, continuously improving their performance.
Types of AI Agents AI agents vary in complexity and include:
- Model-based AI reflex agents: Use an internal model of the environment to make informed decisions based on current and past experiences.
- Goal-based AI agents: Designed to achieve specific objectives by generating and executing plans.
- Utility-based AI agents: Evaluate the potential success of actions using a utility function, considering factors like efficiency, cost, and speed, making them ideal for optimization.
- Hierarchical AI agents: Work collaboratively, where higher-level agents break down tasks for lower-level agents to execute independently.
- Copilots: Assist human users with real-time support and recommendations, augmenting human efforts with AI-driven insights.
- Autonomous AI agents: Fully independent systems that gather data, make decisions, and execute complex plans entirely on their own.
AI Agent Use Cases are wide-ranging, covering personalized healthcare support, custom banking experiences (including fraud detection), intelligent supply chain management (optimizing logistics), automated content curation, and career development assistance.
The Power of Intelligence: Key Differences and Benefits
AI agents bring a level of cognitive ability that dramatically exceeds even advanced chatbots. While both technologies enhance customer service, automate repetitive tasks, and can leverage LLMs for human-like text generation, the depth of their capability is distinct.
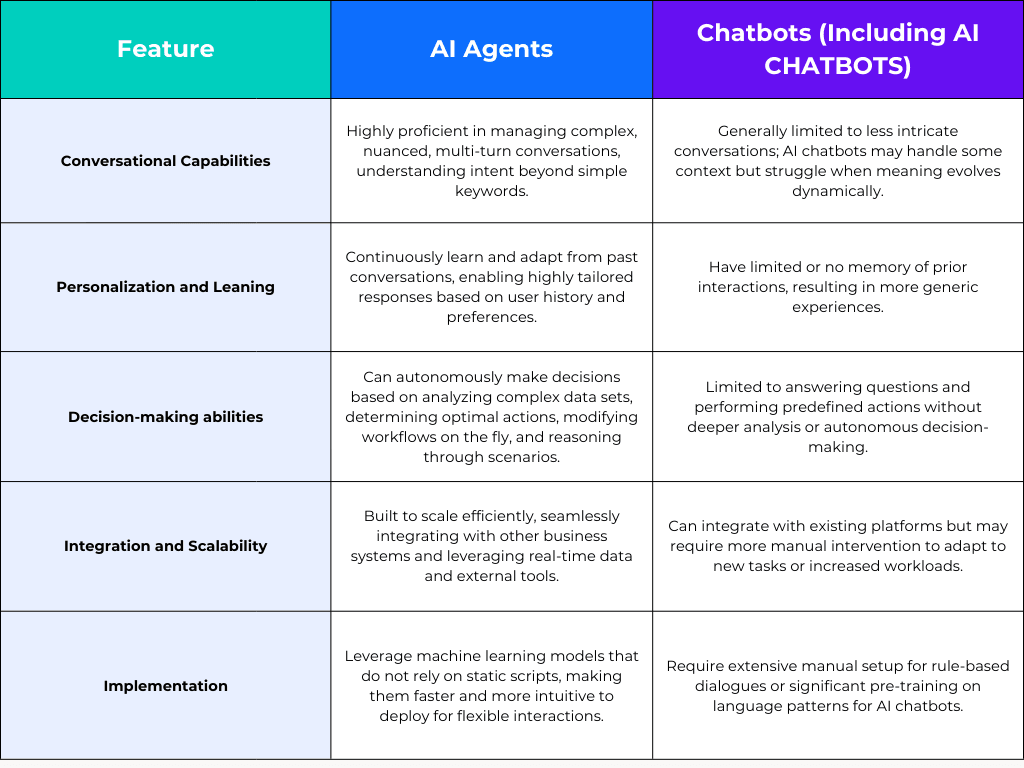
Benefits of AI Agents
By moving to AI agent technology, organizations gain significant advantages:
- Enhanced Efficiency: AI agents process large data volumes and handle multiple tasks simultaneously, improving operational speed and minimizing errors in complex scenarios.
- Higher Quality Outputs: They deliver accurate, comprehensive, and sophisticated solutions by integrating data from various sources and continuously improving through learning.
- Reduced Costs: Automating complex workflows minimizes human errors and reduces reliance on manual labor, cutting down operational expenses.
- More-informed Decision-Making: Leveraging data analysis and machine learning, AI agents provide data-driven insights that lead to faster and more accurate business decisions.
- Reliable Consistency: AI agents consistently produce uniform outputs, crucial for precision tasks like financial analysis or technical support, thereby maintaining high service standards.
Implementing Smart Workflows: Choosing the Right Solution. Organizations must carefully weigh their resources, use cases, and long-term goals when choosing between a chatbot and an AI agent.
Strategic Considerations
The choice should align with the organization's strategic vision, balancing immediate needs with long-term goals. Key factors include:
- Complexity of Use Case: For basic needs like answering FAQs, a chatbot may suffice; for complex workflows requiring decision-making and in-depth data analysis, an AI agent is more suitable.
- Personalization Needs: AI agents excel at offering customized, context-aware communication, which is necessary if adaptive interactions are demanded.
- Budget: Chatbots are generally more cost-effective to implement and maintain, whereas AI agents typically come with higher development and operational costs due to their advanced features.
- Scalability: AI agents are better designed to handle evolving, increasingly sophisticated tasks and offer better long-term solutions than chatbots, which may struggle to scale efficiently.
- Data Privacy and Security: AI agents' broader system access may require more comprehensive security measures than chatbots, which are generally easier to protect due to their narrower scope.
Challenges to Successful Implementation
Regardless of the choice, organizations must plan for common challenges:
- Data Protection: Since AI systems handle sensitive data, organizations must implement advanced encryption, regularly audit access permissions, and comply with regulations like GDPR or HIPAA to mitigate risks of breaches and penalties.
- Insufficient Technology Infrastructure: AI chatbots and agents require significant computing power. Businesses should evaluate current IT capabilities and consider cloud-based SaaS or PaaS solutions, potentially collaborating with experienced technology partners, to handle the demands of AI systems.
- Compatibility and Integration: Achieving seamless integration with legacy back-end and existing customer service systems can be complicated; thorough system compatibility assessments and the use of APIs or middleware can facilitate smooth data exchange.
ServiceNow for AI Agents and Chatbots
ServiceNow provides a comprehensive, integrated solution built on the Now Platform for organizations ready to realize the benefits of automated intelligence.
For handling routine queries and simple tasks, the ServiceNow Virtual Agent serves as an AI chatbot. It enhances user support experiences by delivering personalized, conversational exchanges powered by generative AI and supported by Natural Language Understanding (NLU). The Virtual Agent comes prebuilt with customizable conversations and is fine-tuned for ServiceNow workflows.
For organizations requiring the highest level of intelligence and flexibility, ServiceNow AI Agents offer advanced capabilities to manage the most complex workflows. These agents are designed to handle operations fully autonomously, adapt to evolving requirements, and deliver highly personalized user experiences. Features such as custom agent creation, progressive learning, and detailed governance and analytics ensure businesses can deploy intelligent solutions while remaining fully in control.
Conclusion
Automation is no longer about simple scripts or static chatbots. The modern enterprise requires intelligent systems capable of understanding intent, making decisions, and executing complex workflows. ServiceNow provides both conversational automation (Virtual Agent) and full autonomy (AI Agents), powered by Now Intelligence and enterprise-grade governance.
Organizations that adopt AI agents will unlock greater efficiency, personalization, and scalability ultimately transforming how work gets done.